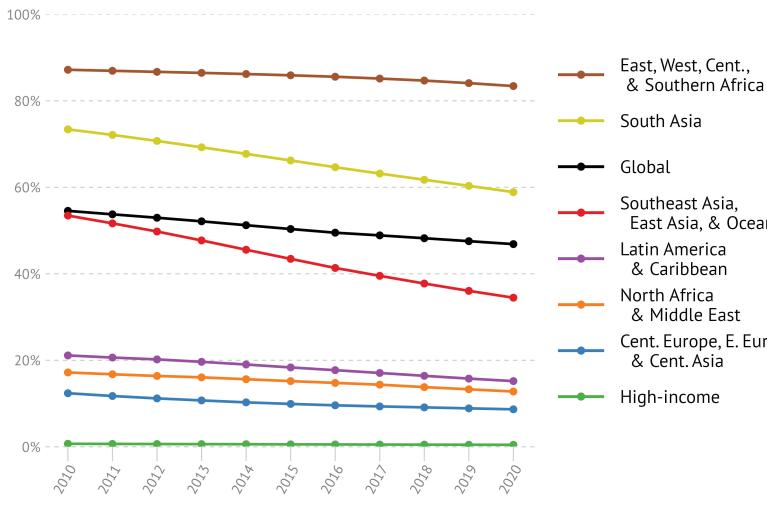
About Household Air Pollution
Household air pollution exposure results from burning solid fuels for cooking, heating, or other domestic tasks. Burning these fuels produces an array of health-harming pollutants, including PM2.5 and its constituent black carbon and carbon monoxide.
The health effects of exposure to HAP include an increased risk of ischemic heart disease, lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lower respiratory infections (such as pneumonia), stroke, type 2 diabetes, and adverse birth outcomes. Exposure to HAP is also associated with the development of cataracts.